How to manage Hiatal Hernia naturally ?
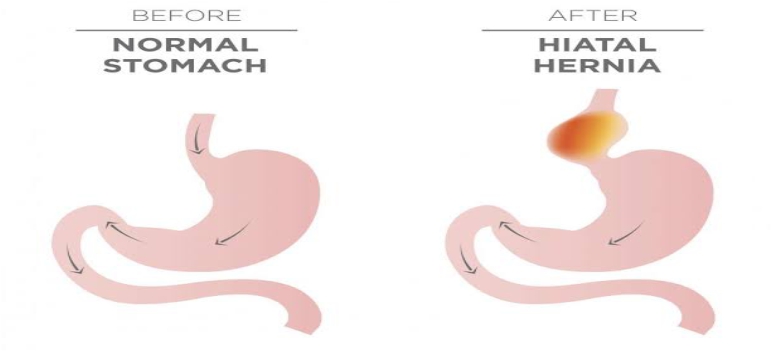
Hiatus hernia, a condition where part of the stomach protrudes into the chest through the hiatus, demands a thorough exploration of its symptoms, root causes, and innovative remedies. This comprehensive guide aims to provide fresh insights for a better understanding of hiatus hernia and, consequently, an improved approach to managing and alleviating its effects on well-being.
Symptoms of Hiatus Hernia:
- Nausea: Persistent queasiness is a common manifestation of hiatus hernia, impacting daily comfort.
- Post-Meal Bloating: Uncomfortable fullness after eating, often exacerbated by the herniated stomach.
- Foul Breath: Bad breath arises from regurgitation of stomach contents, affecting oral hygiene.
- Acidic Regurgitation: Backflow of stomach acids, causing acidity and discomfort.
- Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva production may lead to a persistent dry sensation.
- Gum Irritation: Inflammation and discomfort in the gums due to acid exposure.
- Bitter Taste: An unpleasant taste in the mouth is a direct consequence of stomach acid.
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, a hallmark symptom of hiatus hernia.
- Throat Dryness and Soreness: Discomfort and dryness in the throat can be persistent.
- Chronic Coughing: A lingering cough unrelated to other respiratory conditions.
- Discomfort When Lying Down or Bending Over: Symptoms may worsen with specific movements.
- Unexpected Weight Loss: Unexplained reduction in body weight may be a concerning sign.
- Hiccup Difficulty: Difficulty in controlling persistent hiccups.
- Frequent Burping: Increased belching may be a result of disrupted digestive processes.
Causes of Hiatus Hernia:
- Constipation: Straining during bowel movements contributes to the development of hiatus hernia.
- Chronic Coughing: Repeated coughing episodes can weaken the diaphragm.
- Obesity: Excess body weight exerts pressure on the stomach, contributing to herniation.
- High Inflammation: Elevated levels of inflammation in the body may weaken tissues.
- Abdominal or Diaphragmatic Injury: Trauma to the abdomen or diaphragm can lead to herniation.
- Recovery from Abdominal Surgery: Post-surgical complications may increase the risk.
- Muscle Weakness in Older Age: Natural aging processes contribute to weakened muscles.
- Poor Diet: Unhealthy eating habits, including low fibre intake, maybe a contributing factor.
Progressive Remedies for Hiatus Hernia:
-
Smoking Cessation: Smoking exacerbates inflammation and impairs muscle reflexes, making it crucial to quit for hiatus hernia management.
-
Sleep Position Adjustments: Avoid lying down for several hours after meals. Elevate the head of the bed to control stomach content flow, promoting better digestion.
-
Regular Exercise: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiding in sound sleep, promoting digestive health, and reducing inflammation.
-
Maintaining Healthy Weight: Obesity puts additional pressure on the stomach, making weight management essential. Adopt a balanced diet and regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight.
-
Incorporating Nutrient-Rich Foods:
- Vegetables: Include fresh, organic vegetables such as squash, leafy greens, cucumbers, asparagus, and artichoke.
- Probiotic Foods: Integrate kefir and yogurt for improved digestive health.
- Fruits: Choose melons and berries to prevent the worsening of hiatus hernia symptoms.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for wild fish and free-range chicken to support overall health.
-
Avoidance of Trigger Foods:
- Spicy Foods: Steer clear of spicy foods that can exacerbate symptoms.
- Chocolate, Tomatoes, Onions, Garlic: Avoid these trigger foods that may contribute to acid reflux.
- Citrus Fruits: Limit the intake of citrus fruits to minimize acidity.
- Processed Foods: Reduce the consumption of processed foods with high sodium content.
A holistic understanding of hiatus hernia, combined with proactive lifestyle changes, is crucial for effectively managing its symptoms and promoting overall well-being. This approach empowers individuals to take charge of their health, fostering a more comfortable and balanced life
